What Are The Signs and Effects of Receding Gums?

Within this blog, we will be covering all the key points to know about the signs and effects of receding gums. This includes what gums are, the causes of gums receding, potential risk factors, the signs and effects of gums receding and how to prevent gums receding.
What are gums?
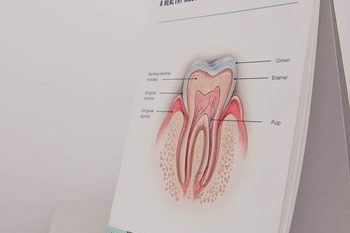
To understand receding gums, we must first look at what gums are. The gums, or gingivae, are comprised of pink tissue which is within the mouth and meets the base of the teeth. Each set of teeth has one gum/gingiva. Gingival tissue itself is dense and possesses a strong supply of blood vessels under a moist surface, which is called the mucous membrane. The gingival tissue connects with the rest of the mouth lining.
The gums themselves are securely joined to the jawbone and help to tightly cover each tooth, all the way up to the neck. As long as the gums remain undamaged then they are able to cover the roots of teeth and safeguard them. Receding gums occurs following a loss of gum tissue, subsequently exposing the roots of teeth to issues such as bacteria/plaque and potential decay.
Causes of receding gums
A key cause of receding gums is a lack of good oral hygiene and periodontal disease, although the issue can occur in those with good oral hygiene also. Another key issue is the physical wearing down of the gums and subsequent inflammation of the tissues. Inherited factors can also play a role for example, effecting the position of the teeth and thickness of the gums themselves.
Forceful tooth brushing and using stiff bristles can also lead to receding gums. This particular type of physical recession usually impacts the left side of the mouth primarily. This is due to the majority of individuals being right-handed, thus left gums have more pressure exerted on them. Side gums are also usually affected more than the front gums with this type of recession.
Other physical factors which may cause gum recession are piercings in the mouth, poor teeth alignment, and potential damage from dental treatment. Some individuals may be more prone to receding gums if they have delicate gum tissue which can become inflamed easily. Additionally, a thin gum can mean plaque is more easily able to inflame them. If plaque does build up on the teeth, it not only causes inflamed gums but also potential periodontitis, and even periodontal disease.
Potential risk factors
There are several potential risk factors that affect your likelihood of receding gums, these are listed below:
- Overzealous tooth brushing: Traumatic brushing habits can give rise to gum loss, and it is often seen preferentially on the opposite side of the mouth to the patient’s dominant hand (e.g. recession on the left more than the right side may indicate a traumatic brushing habit).
- Diabetes: This can play a key role in receding gums and increases your chances.
- Age: Your age can play a key role in receding gums, with almost 90% of individuals above the age of 65 having some receding gums in at least one area.
- Genetics: Those who possess thin/weak gums can potentially pass this on to offspring and thus increase the chances of receding gums via genes.
- Periodontal/ Gum Disease: Those patients with gum disease are more prone to recession
- Smokers/Tobacco users: Chances of receding gums are greatly increased if you smoke or use tobacco in any way.
Signs and effects of receding gums
It is often the case that many individuals that have receding gums may not even be aware they have an issue and thus cannot take precautionary measures. Some signs and effects have been listed below to look out for.:
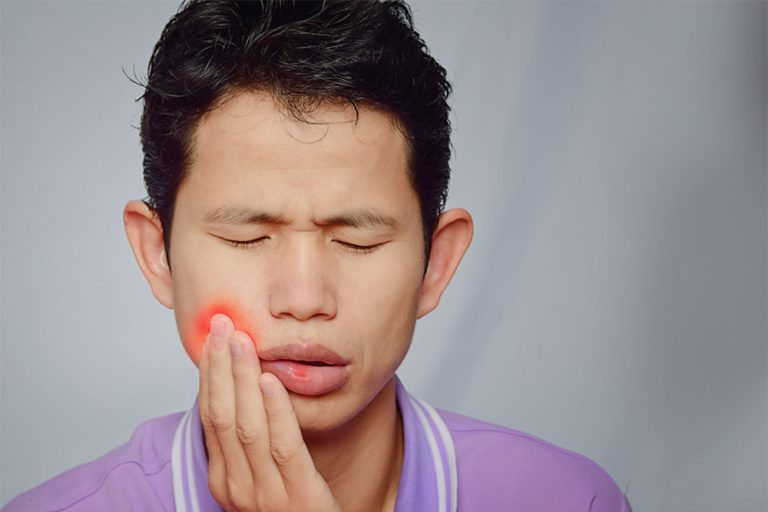
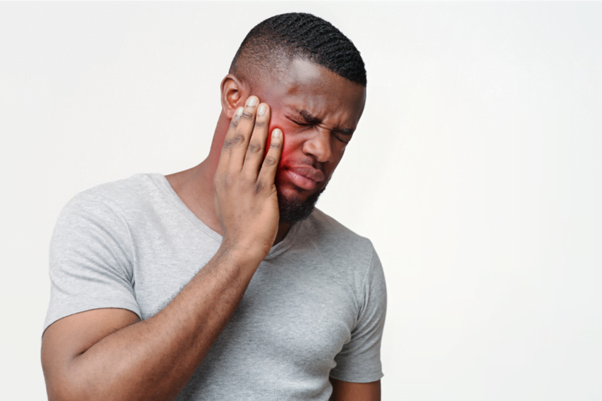
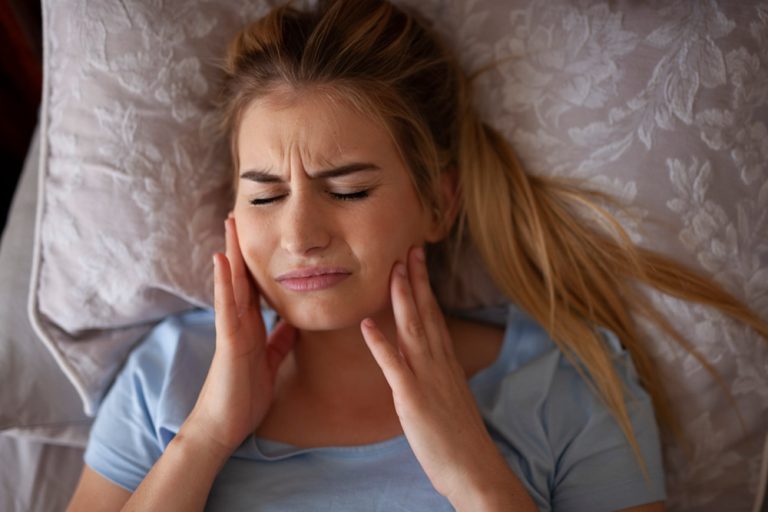
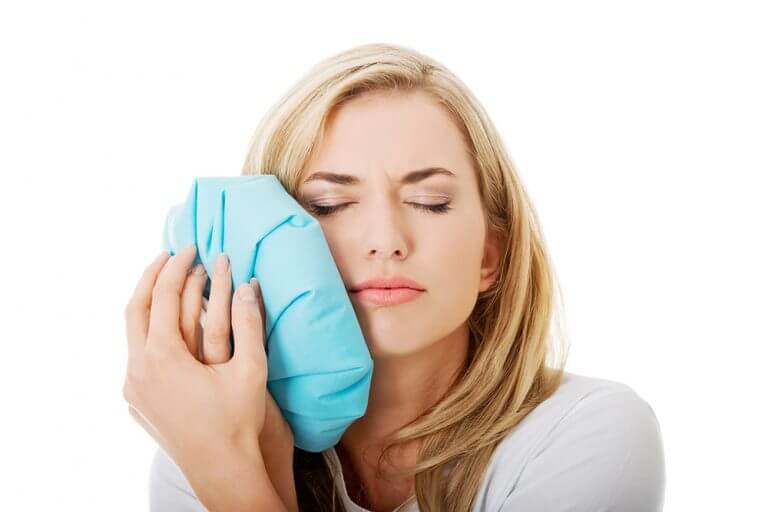
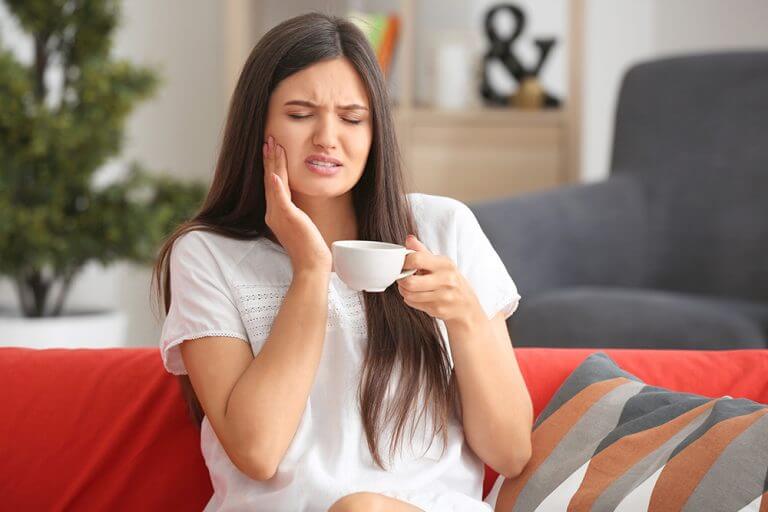
- A key sign/effect of receding gums is a sensitivity to the cold or heat as the exposed tooth roots would become extremely sensitive as gums recede.
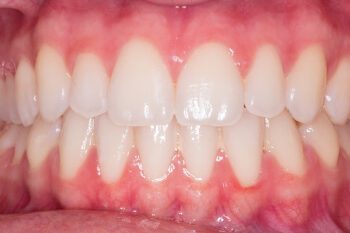
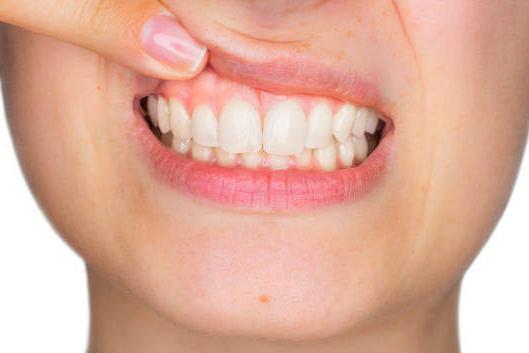
- Changing appearance of your teeth/gums, this includes teeth potentially appearing longer or the space between teeth increasing fairly significantly.
- Teeth loss can also be a sign that your gums are receding significantly.
- Tooth decay and subsequently bad breath and bleeding gums are also key effects from gum recession and may also indicate other gum diseases.
Preventing gums receding
In most scenarios, gums receding is a preventable issue and as long as signs/effects are spotted early then it can be halted all together. Perhaps the biggest preventable cause is brushing the teeth too abrasively or using a particularly abrasive toothbrush. This cause can be easily prevented through using a very soft toothbrush and brushing gently rather than harshly when possible.
Allowing a significant level of plaque to build-up and become tartar is also very preventable and can also avoid further issues such as periodontal disease. This issue can be dealt with by maintaining impeccable oral hygiene and regularly visiting the dentist. If you have any concerns about your gums potentially receding or if you spot any signs/effects of gum recession, then you should contact your dentist as quick as possible to avoid future issues.
If it has been a while since your last visit to the hygienist, why not make the call today.
Call 020 3925 3846 or fill in our form to enquire about your consultation.